Networking - Assign static IP Address for a FileWave Appliance
For the Linux based BoosterFileWave Server, Booster, or IVS if you cannot use the port https://server:10000 to change network setting please follow the instructions below:
Debian Linux
Debian Linux
Changing the IP address in Debian 12, which uses systemd-networkd for network management, involves different steps compared to CentOS. The following guide is tailored for Debian 12 servers using systemd-networkd but you could also use Webmin on your server assuming the server comes online initially with DHCP.
For Webmin know that you will need to go to Webmin -> Webmin Configuration -> Operating System and Environment and make sure it's set to Debian 12.4 (Or whatever version we are at when you set up your system. You can see this with cat /etc/debian_version on the server.
- Locate Network Interface:
First, identify the network interface you wish to configure. You can list all network interfaces using:
networkctl list - Configure Network Settings:
systemd-networkduses individual.networkfiles for each network interface, located in/etc/systemd/network/.
Create or edit the network configuration file for your interface, named like
10-eth0.network(replaceeth0with your interface name).sudo nano /etc/systemd/network/10-eth0.network - Configure IP Address:
In the.networkfile, add or modify the following sections:
Replace[Match] Name=eth0 [Network] Address=192.168.1.100/24 Gateway=192.168.1.1 DNS=8.8.8.8 DNS=8.8.4.4 LinkLocalAddressing=no IPv6AcceptRA=noeth0with your actual network interface name.
Modify theAddresswith your new IP and subnet mask (e.g.,/24for a 255.255.255.0 netmask).
Set theGatewayandDNSentries as per your network configuration.
You'll also want to edit/etc/network/interfacesbecause ens192 is configured there for DHCP. That's how you might have gotten to it via Webmin for instance. Edit the file to put a # before the 2 lines that have ens192 on them. Those 2 lines in the file will look like this after editing:
# The primary network interface #allow-hotplug ens192 #iface ens192 inet dhcp -
Reload and Restart systemd-networkd:
After making changes, enable the Networkd service so interfaces come up at boot time, and reload the daemon and restart the network:
sudo systemctl enable systemd-networkd sudo systemctl daemon-reload sudo systemctl restart systemd-networkd - Verification:
Check the status of your network interface to ensure the new settings are active:
networkctl status eth0You can also useip addr show eth0to view the IP configuration.
Related CentOS Linux
CentOS Linux
Depending if you are using the appliance we offer for a CentOS Linux virtual appliance or a Linux machine you built the steps may be slightly different. The steps shown below will be for the FileWave virtual appliance that we offer.
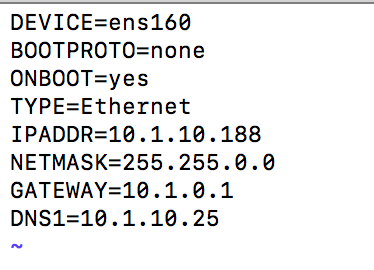
Configure the "ifcfg-ens160" file on the server. (This file will be different if you are not using our Virtual Appliance and will have a different name like "ifcfg-eth1" for example)vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens160Change/add the following values of the file.Change BOOTPROTO=noneAdd "IPADDR", "NETMASK", "GATEWAY", "DNS1" to the file with your network configurations. I attached a screen shot of a completed file below. (If you want to add more then one DNS server you can add DNS2, etc to the file)Save the file using "esc" then ":wq"
Now you will need to restart the network services on the server./etc/init.d/network restart