Booster Installation
Description
Booster software is compatible with either macOS, Windows or Debian. All necessary installers or appliances can be found on the current download pages: FileWave Software Downloads
Installers
Debian
Linux has two options. FileWave provides (as with the FileWave Server) a pre-built Debian VM. Alternatively, it is possible to self-install the software on a Debian system.
macOS & Windows
Installers are available as PKG or MSI.
As typically with MSI installers, options exist not only for install, but repair and deletion
Install Paths
Booster installs the software to one of the following locations:
- Windows: C:\Program Files\FileWave\fwBooster.exe
- macOS, Debian: /usr/local/sbin/fwBooster
Booster Configuration
Once installed, configuration is via the Booster Monitor application, available for both macOS and Windows from the same downloads page.
Note that the standalone application, Booster Monitor, will only be able to connect to a Booster for initial configuration. Once a Booster is configured you must access Booster Monitor from FileWave Central in the Boosters section. This is because authentication is protected, and the FileWave Central application provides a secure connection. Launching Booster Monitor directly would not have that same authentication, and you will see an error about the Booster not running.
Installation
Debian
If using the pre-built Debian Appliance, simply add the VM to the VM infrastructure. Alternatively, follow the commands provided on the downloads page.
macOS & Windows
Run the relevant PKG or MSI installer, accepting any terms and agreements.
Custom Installers may be created, pre-defining details, e.g. Server Address, Port and Booster Monitor Preferences password: Custom Installers
Configuration
Network Address
Configure a static IP for the Booster and consider adding a Domain Name within the DNS for this IP.
macOS and Windows can be configured using the Settings. However, Debian will require some command line configuration.
Debian IP Setup
Network Interface
The current IP may be determined with the 'ip addr' command:
# ip addr
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host noprefixroute
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: ens192: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 00:0c:29:9d:4d:7e brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
altname enp11s0
inet 192.168.1.98/24 brd 192.168.1.255 scope global dynamic ens192
valid_lft 68853sec preferred_lft 68853sec
inet6 fe80::20c:29ff:fe9d:4d7e/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft foreverThe key part here is the name of the network interface. In the above example, this is 'ens192'.
Edit Network File
Make a backup of the current file:
cp /etc/network/interfaces /etc/network/interfaces-mybackupEdit the original file:
sudo nano /etc/network/interfacesAdd the chosen IP and other necessary details for this interface. Given the details above, it may look something like the below once edited:
# This file describes the network interfaces available on your system
# and how to activate them. For more information, see interfaces(5).
source /etc/network/interfaces.d/*
# The loopback network interface
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
# The primary network interface
iface ens192 inet static
address 192.168.1.22
netmask 255.255.255.0
gateway 192.168.1.255
dns-nameservers 8.8.4.4 8.8.8.8Once complete, save and then restart the network service:
sudo systemctl restart networkingRe-running the 'ip addr' command should now show the new details.
Add a name with this IP on the DNS.
Booster Setup
Install the Booster Monitor on a chosen macOS or Windows device. On launching the Booster Monitor, use the above created network address. The initial view is akin to the FileWave Client Monitor, but with Booster specific details:
Select Preferences, enter the created password (or default password as provided from the downloads page)
Consider changing this password at the earliest possible moment
This password is only used to access the Preferences from the Booster Monitor.
The Booster Monitor may then be used to configure the Booster. At a very basic level, the Server Address and port should be added.
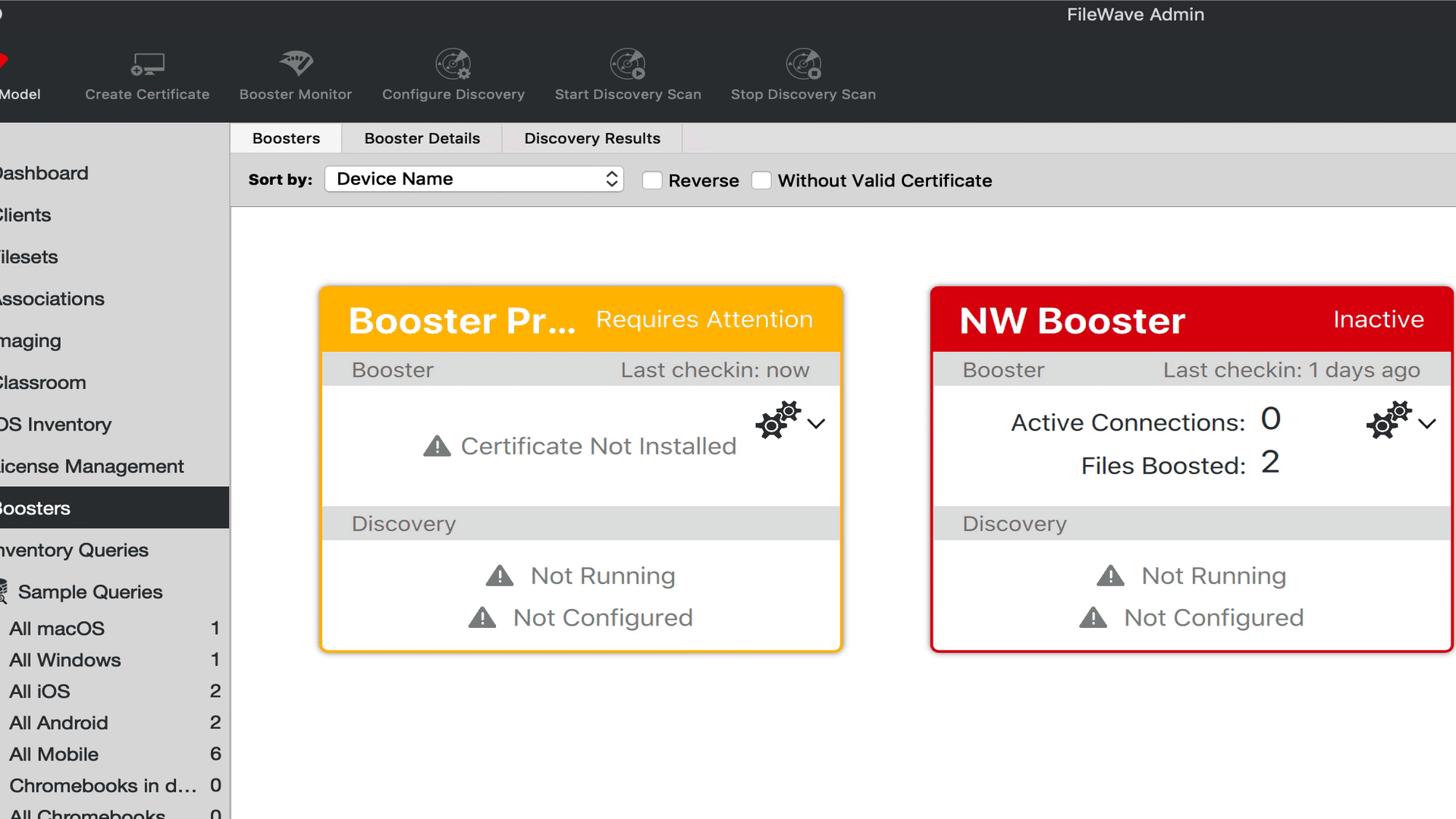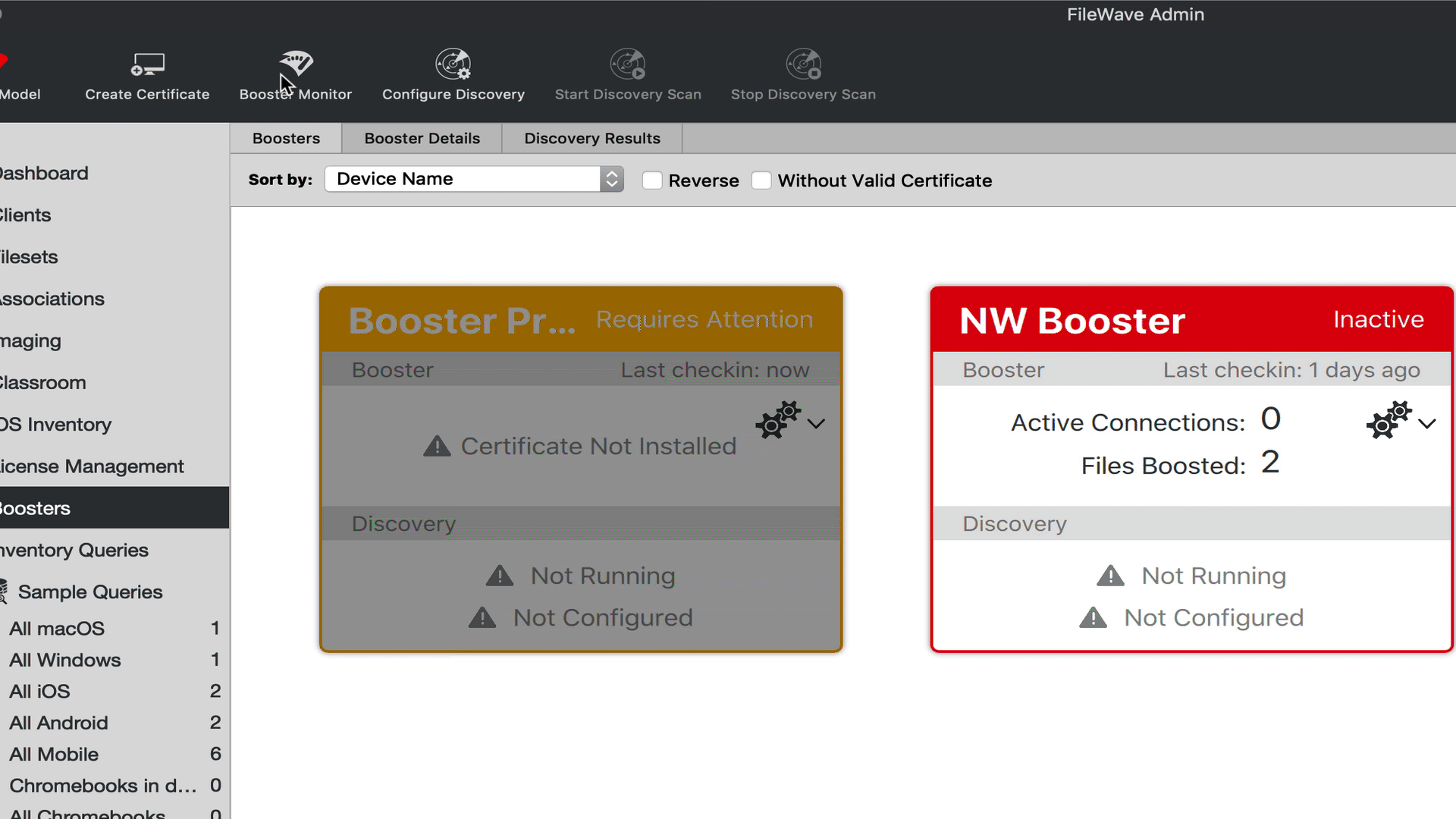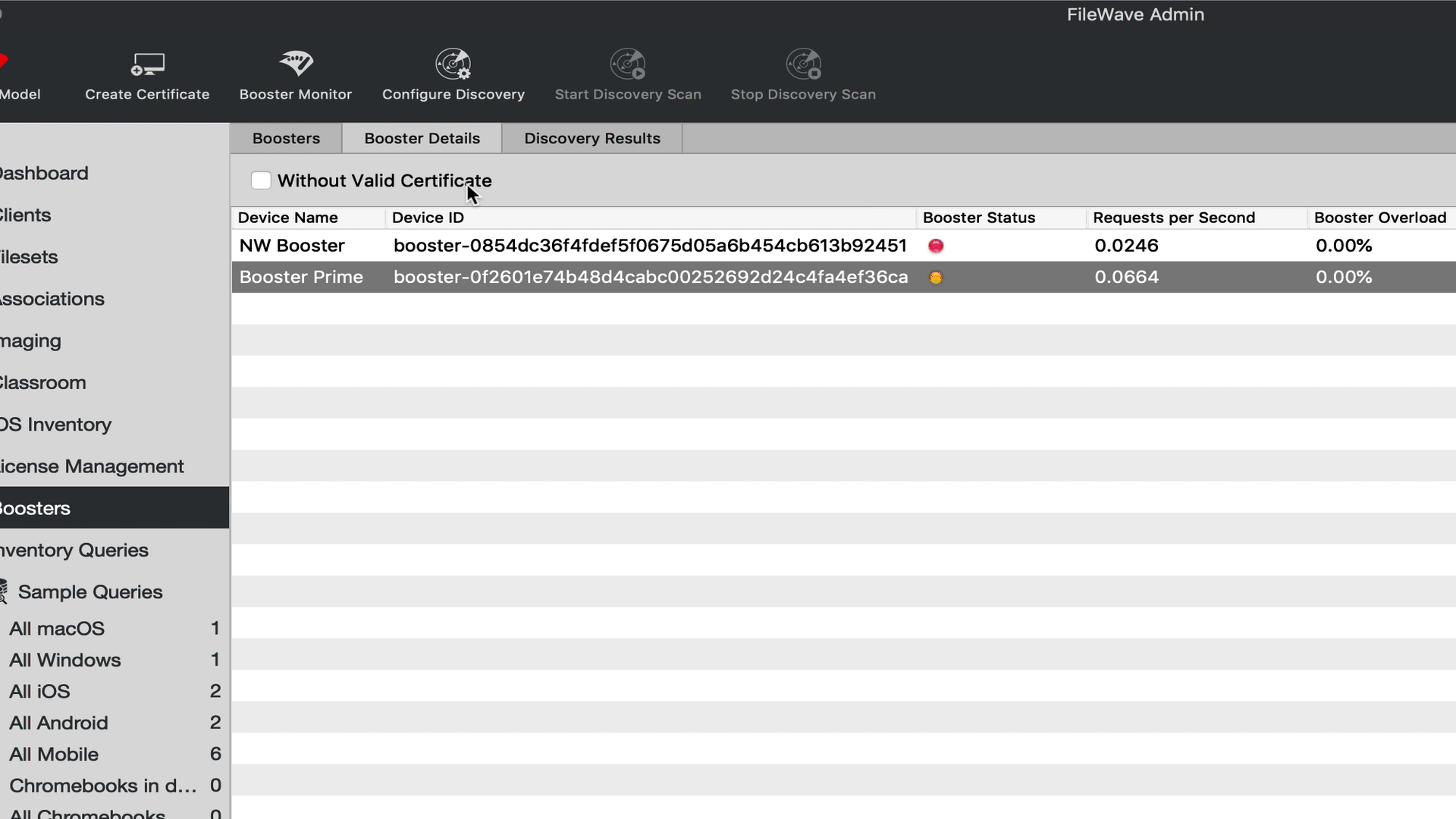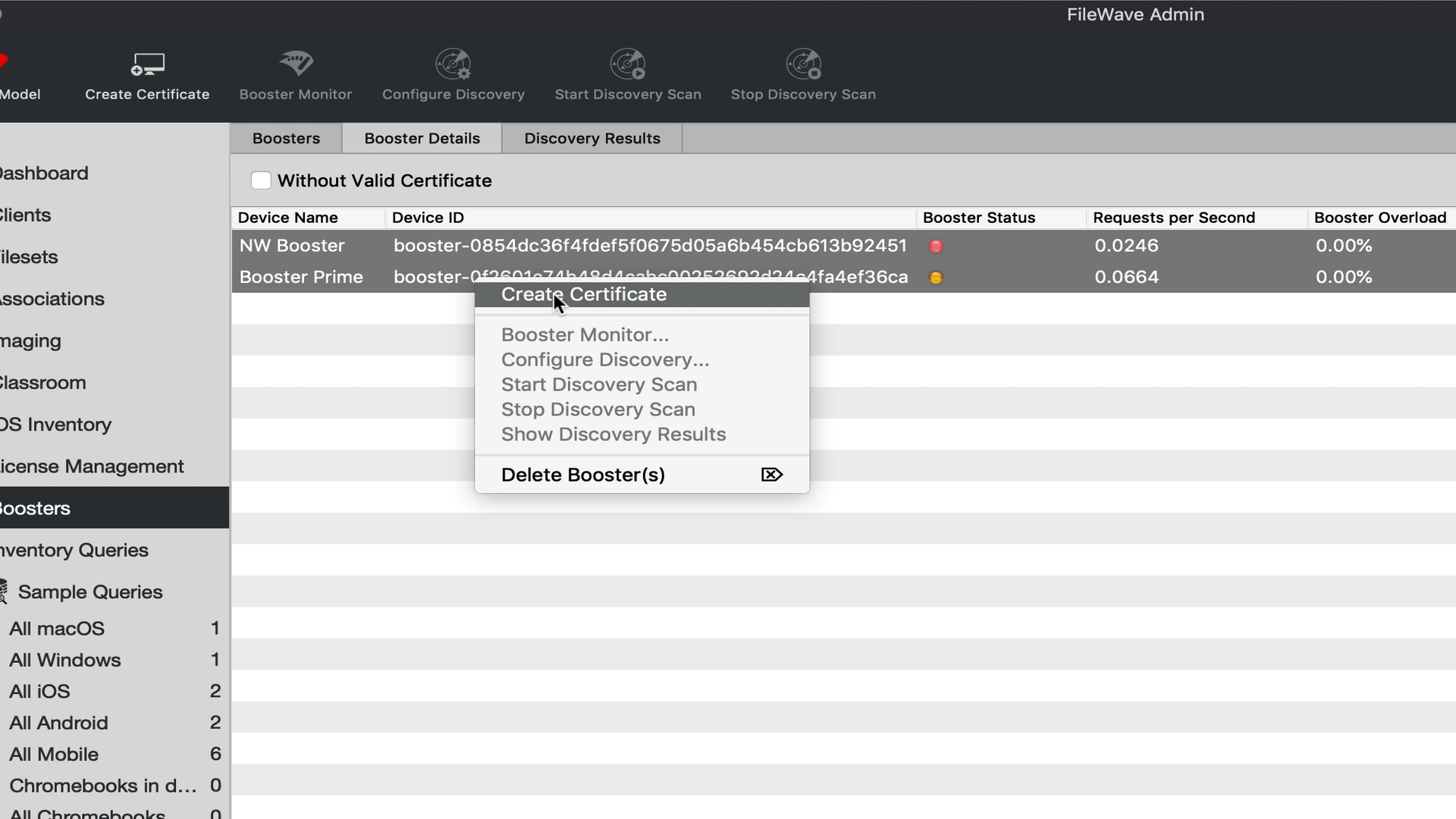
Approving Boosters
Once a Booster is setup on the network with the relevant FileWave Server details, it should then check-in with the server and be visible in the Booster section of the FileWave Central admin application software.
As of FileWave 13.1.0, additional security and certificates were introduced, requiring the approval process.
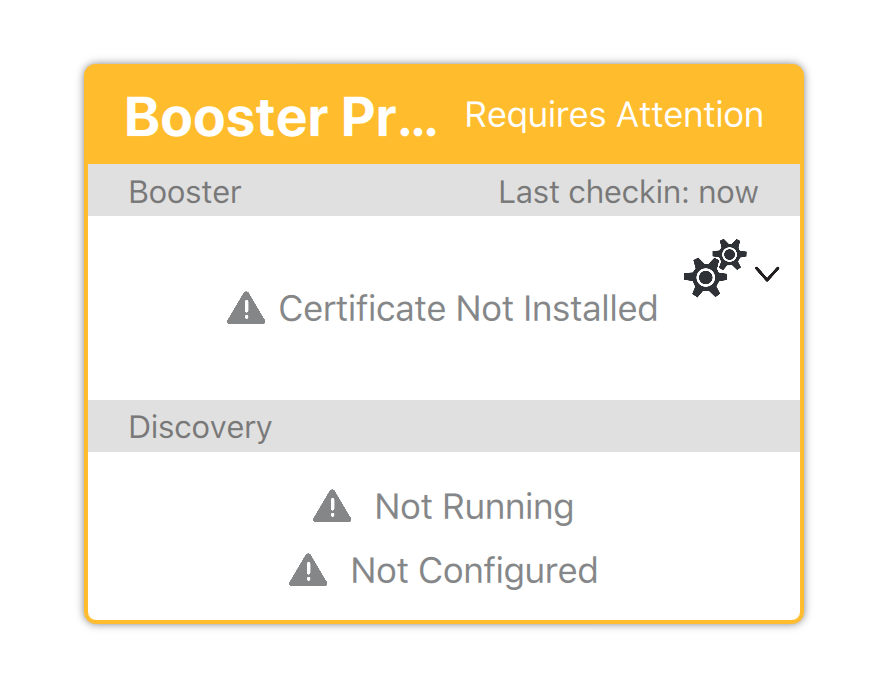
The approval process generates a certificate for the Booster. There are four ways to generate a certificate for a booster.
- Select booster(s) in the Booster view → right-click → Create Certificate/Enroll Booster
- Select booster(s) in the Booster view → Create Certificate/Enroll Booster (in the button bar)
- Select booster(s) in the Booster Details → right-click → Create Certificate/Enroll Booster
- Select booster(s) in the Booster Details → Create Certificate/Enroll Booster (in the button bar)
Booster Deletion
If a Booster were deleted from FileWave, this will revoke the certificate. If still running, on a subsequent check-in, the approval process should need to be re-actioned.


At what version did the "Create Certificate" option change to "Enroll Booster"?
Do both options server the same purpose, and/or are there significant differences between the two?
In reply to #1
It was a change in wording only but serves same function.
No comments to display
No comments to display