Setting up the IVS (Imaging Virtual Server)
Guide for Networking Imaging with FileWave
The following steps will assist you in the setup and implementation of your Imaging Virtual Server (IVS)
If you already have your Imaging sever up and running please look at these guides for how to image Windows devices.
*Please note: This document assumes you have already set up your FileWave Management Server.
Prepare and download all needed parts
Before starting be sure you have:
-
Downloaded the latest Imaging Virtual Server (IVS) linked here
-
A running FileWave server with clients enrolled (or with placeholders)
-
FileWave Admin installed on your workstation
-
Valid MAC Address for each Windows machine
-
Virtual Environment (e.g. ESXI, Virtualbox, VMware Fusion)
-
No Firewall between your VLANS or access to the Inter-VLAN Firewall to open Ports specified below
IVS capabilities:
-
UEFI compatibility
-
Multiple partitions per image
-
GBT and MBR disks can be imaged
-
Image a blank disk
-
Windows 10 and 11 (including non-UEFI, UEFI with CSM and native UEFI machines)
-
Check if the Windows partition is in hibernated or fast restart state before creating master image
-
Imaging logs are copied to IVS in order to ease imaging issues troubleshooting
Network Considerations
Subnets
The FileWave Imaging appliance has to be configured as an “ip-helper” on your switches so it can receive and answer BOOTP requests from your clients.
The FileWave network imaging solution is unicast so there will need to be some preparation on your end if you intend to image across multiple subnets. The two options will be:
A. Install a separate FileWave Imaging Virtual Server (IVS) on each subnet you plan to image from and connect them all to the FileWave server by following the "Connecting IVS to FileWave Server" section in this document.
B. Setup "Helper IPs" on your layer 3 devices (e.g. routers, routing switches) that will point the broadcast requests for PXE and Netbooting to your single FileWave IVS. Once this has been completed you will need to make a change on the IVS. To do this either open the console for this server in your virtual environment or ssh into the server with Putty (Windows) or terminal (macOS):
-
-
Open terminal (If on Windows you can use Putty linked here and use the credentials root/filewave (FileWave 15.4.2 and older) or fwadmin/filewave (FileWave 15.5.0 and beyond) then skip to step 3 below)
# replace IVS-IP-Address with your IP address # replace fwadmin with root if your Appliance is pre-15.5.0 $ ssh fwadmin@IVS-IP-Address -
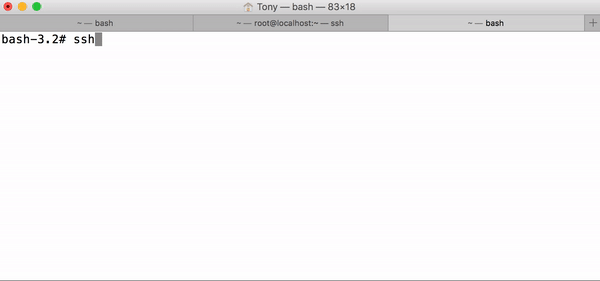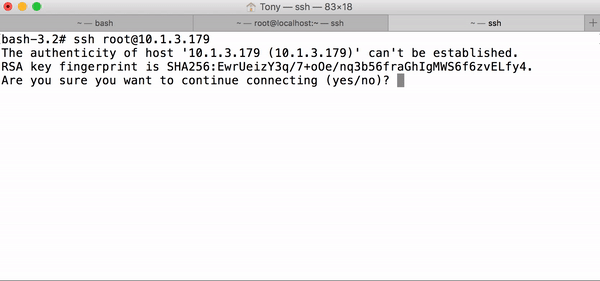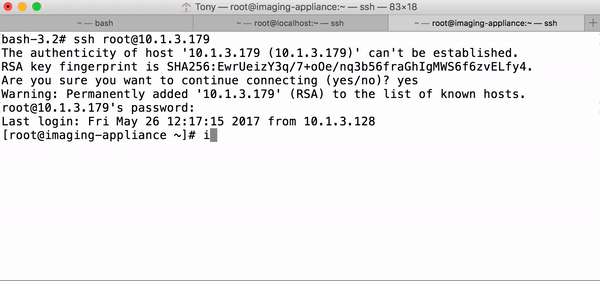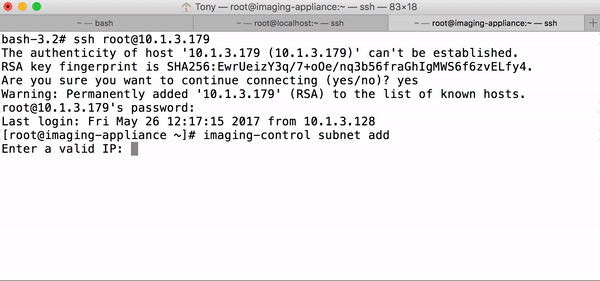
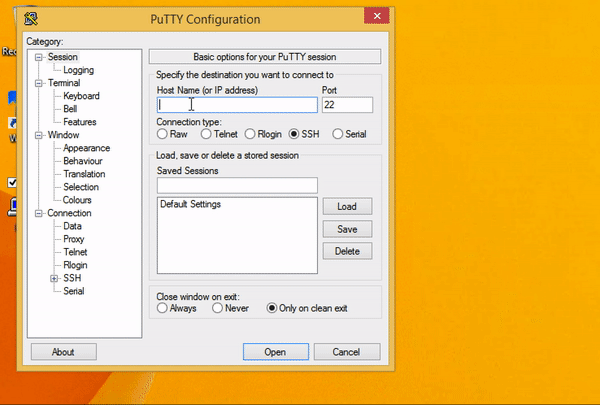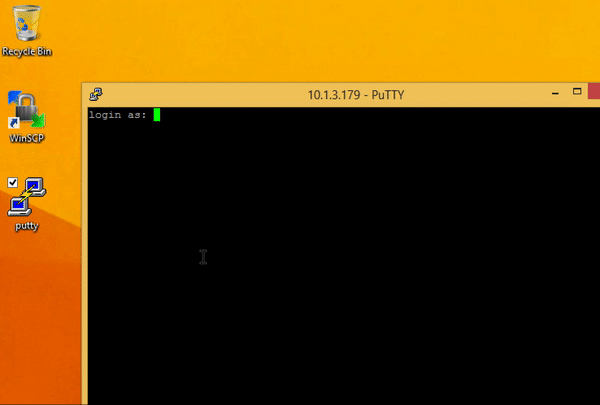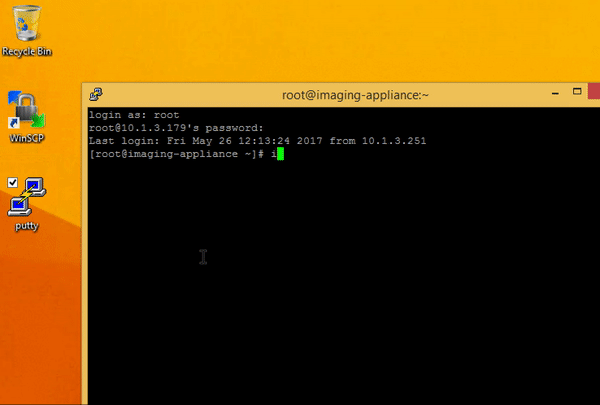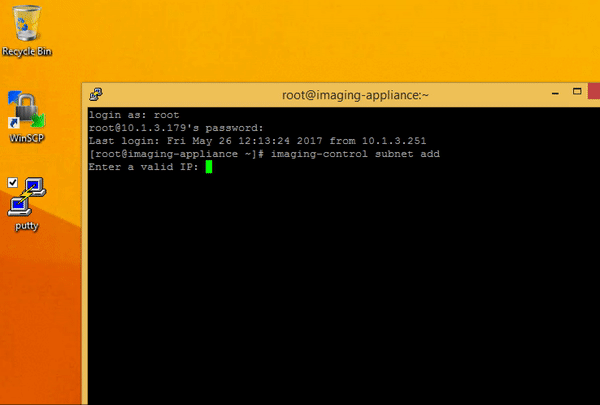
Type the following command
-
# enter in imaging-control subnet add to add your subnet addresses $ imaging-control subnet add -
This will prompt for a valid IP address from the subnet and subnet mask
Note: use command imaging-control subnet remove to remove a subnet
-
Firewall
The IVS needs to be able to connect to your FileWave Server on the following Ports
-
20017
-
20443
-
20445
Any client(s) subnets where imaging should work must be able to reach the following Ports on the IVS:
-
67 (DHCP), 69 (TFTP)
-
80 (HTTP)
-
20444 (HTTPS)
-
111 (TCP,UDP)
- 2049 (TCP,UDP) used by default (When VPN is not used for NFS)
-
20490 (TCP,UDP) used for VPN to NFS access
Any machine running FileWave Central needs to be able to connect to your IVS on the following Ports:
- 20010 (Client Monitor), 20444 (Remote Configuration, Shared Keys)
The FileWave Server must be able to reach the IVS on port 20444 for On-Premise customers.
Starting the Imaging Appliance for the first time:
-
Download the latest Imaging Virtual Server (IVS) linked here
-
Import the Imaging Virtual Appliance (IVS) into your virtual environment or use a player to start up the machine. Note: If you need help on this please use the import guides linked here.
(If you used the linked KBs to import the IVS, the following steps should already be complete and you can move on to the next section, Connecting the IVS to the FileWave Server) -
When the server starts up it will display the IP address, be sure to make a note of this.
Note: Should the machine get stuck during boot, showing a white bar at the bottom please send a CTRL-ATL-DEL to the machine. The second boot should be much quicker. - If importing version 15.5+, you will be prompted at first boot to change the default password. Please see Setting the Password on First Login to FileWave Appliances (15.5+) for more details. If you're importing an older appliance, please see the first drop-down below to change the default password to something more secure.
- Change the IP of the IVS to a static IP address using the second drop-down below.
Changing 'root' Password on Older IVS Versions (pre-15.5)
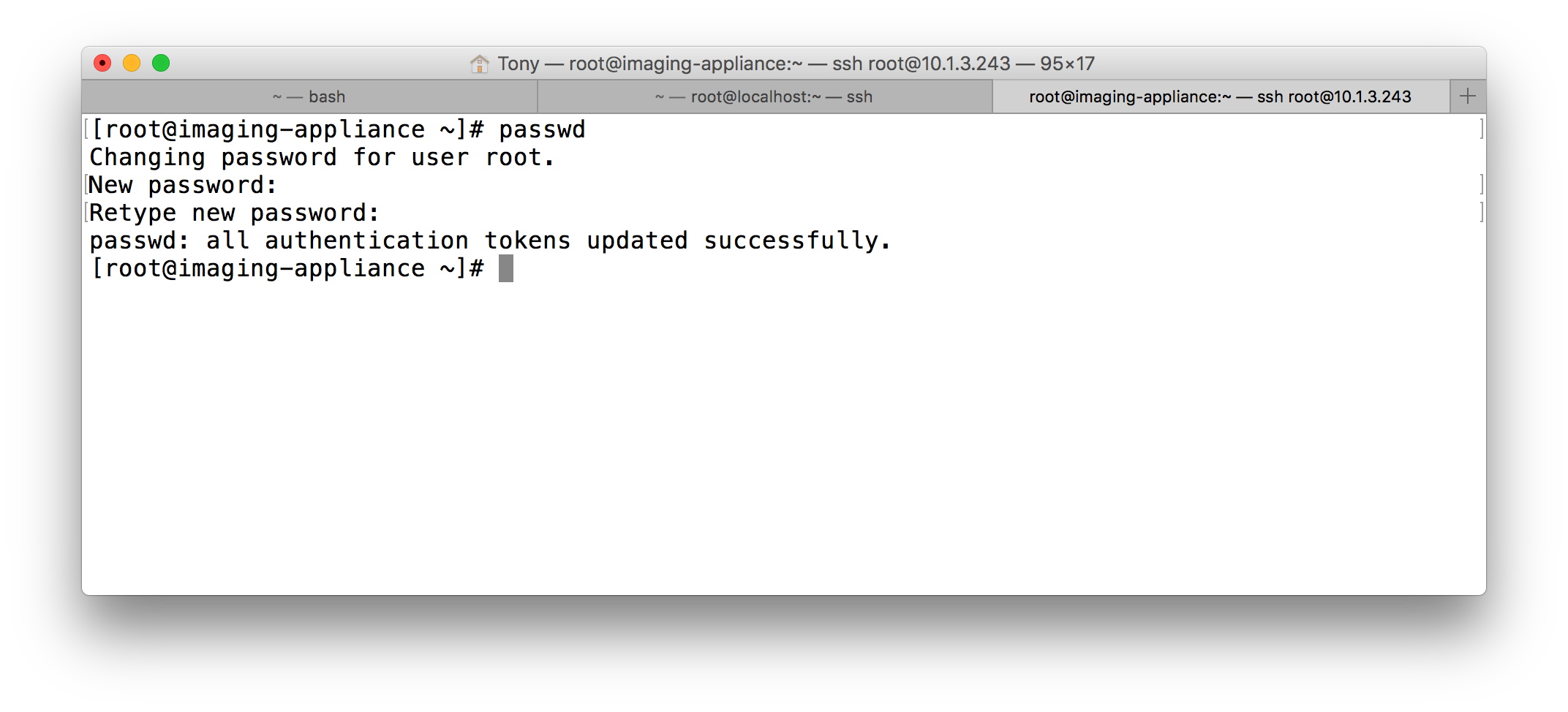
Login to the IVS (either console or SSH) and change the default password from what is currently filewave to your own.
-
Type in the following command, when prompted for a password use 'filewave':
# replace IVS-IP-Address with your IP address $ ssh root@IVS-IP-Address -
Then type the command below to enter your new password
$ passwd - Enter new password
Changing the IP of the IVS Server to Static
1. Locate Network Interface:
First, identify the network interface you wish to configure. You can list all network interfaces using:
networkctl list2. Edit the /etc/network/interfaces file: Using 'nano', edit the interfaces file to set the network configurations.
nano /etc/network/interfacesYour default interfaces file should look something like this (your interface name may be different):
# The loopback network interface
auto lo eth0
iface lo inet loopback
# The primary network interface
iface eth0 inet dhcp
Change the file to look like this, using your network preferences (note 'dhcp' has been changed to 'static' in line 6)
# The loopback network interface
auto lo eth0
iface lo inet loopback
# The primary network interface
iface eth0 inet static
address 192.168.10.33
netmask 255.255.255.0
gateway 192.168.10.255
dns-nameservers 192.168.10.254 192.168.10.2553. Verify Resolv.conf, hosts and hostname files: Verify that these files in /etc/ are configured correctly for your network and server.
/etc/resolv.conf: This file should list your DNS servers
/etc/hosts: This file should point your FQDN to localhost (127.0.0.1) - Below is an example of what the file looks like on ivs1.filewave.net for example. Notice the 2 entries for loopback. Although IPv6 should be disabled, it is good to include the IPv6 loopback in case it is ever enabled.
127.0.0.1 localhost
::1 localhost ip6-localhost ip6-loopback
ff02::1 ip6-allnodes
ff02::2 ip6-allrouters
127.0.0.1 ivs1.filewave.net
::1 ivs1.filewave.net/etc/hostname: Specifies the hostname for your server. This is filewave by default.
4. Disable IPv6: Edit the sysctl.conf file by adding the following lines to the end of the file:
nano /etc/sysctl.confnet.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6 = 1
net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6 = 1
net.ipv6.conf.lo.disable_ipv6 = 1
net.ipv6.conf.tun0.disable_ipv6 = 15. Restart/Check Network Status:
systemctl restart networking.service
systemctl status networking.service6. Verify IP:
ip a
Connecting the IVS to the FileWave Server:
If you are a FileWave Hosted Customer, you need to review the following before connecting the IVS to the FileWave Server: FileWave Hosted Servers and IVS Setup
-
Open and connect your FileWave Admin to your FileWave server
-
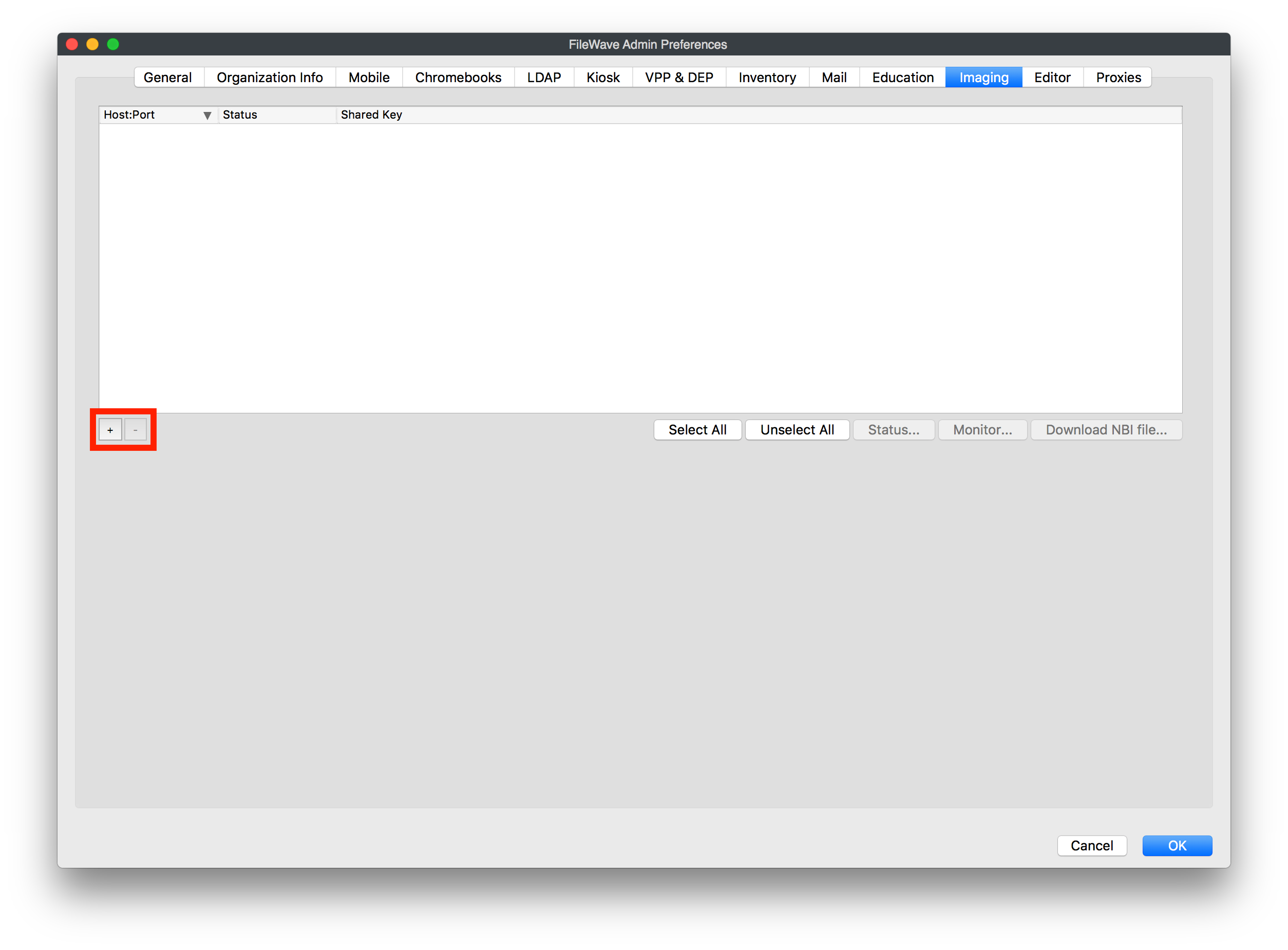
Open the preferences and go to the "Imaging" tab
-
Hit the "+" at the bottom left of the blank pane
-
Enter the IP address of the IVS into "Preference for Imaging"
-
Make sure the box marked "generate new key" is now checked and click "OK"
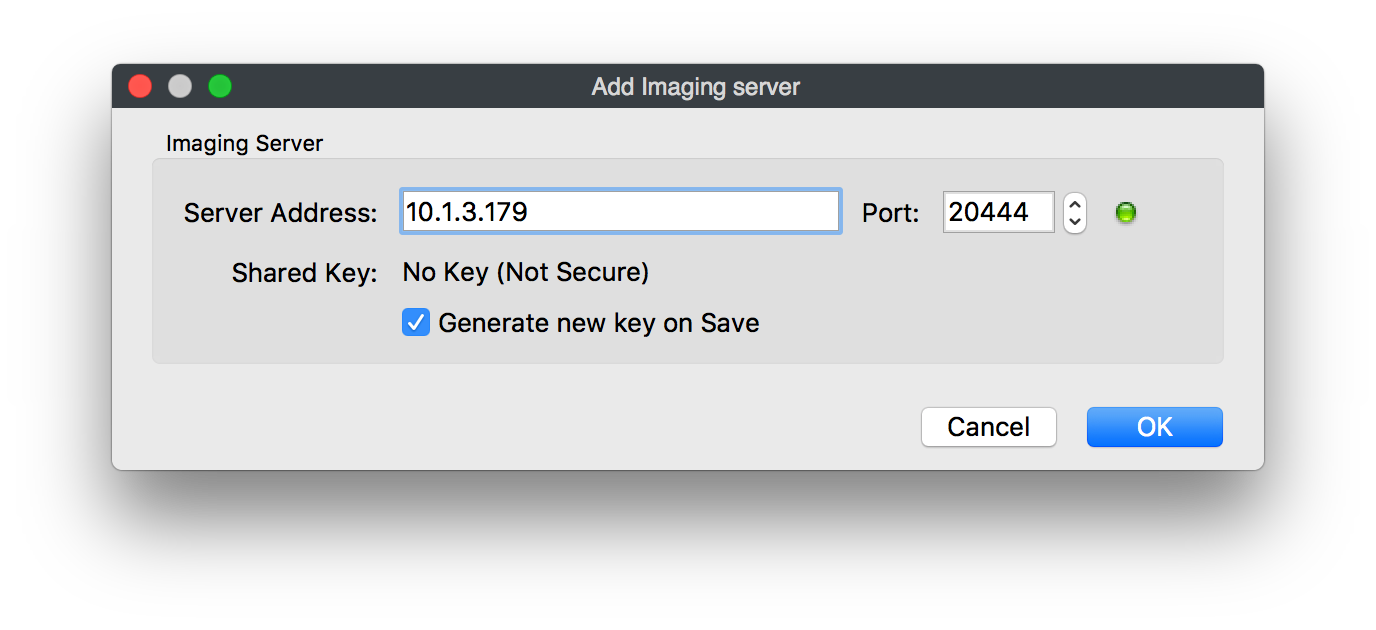
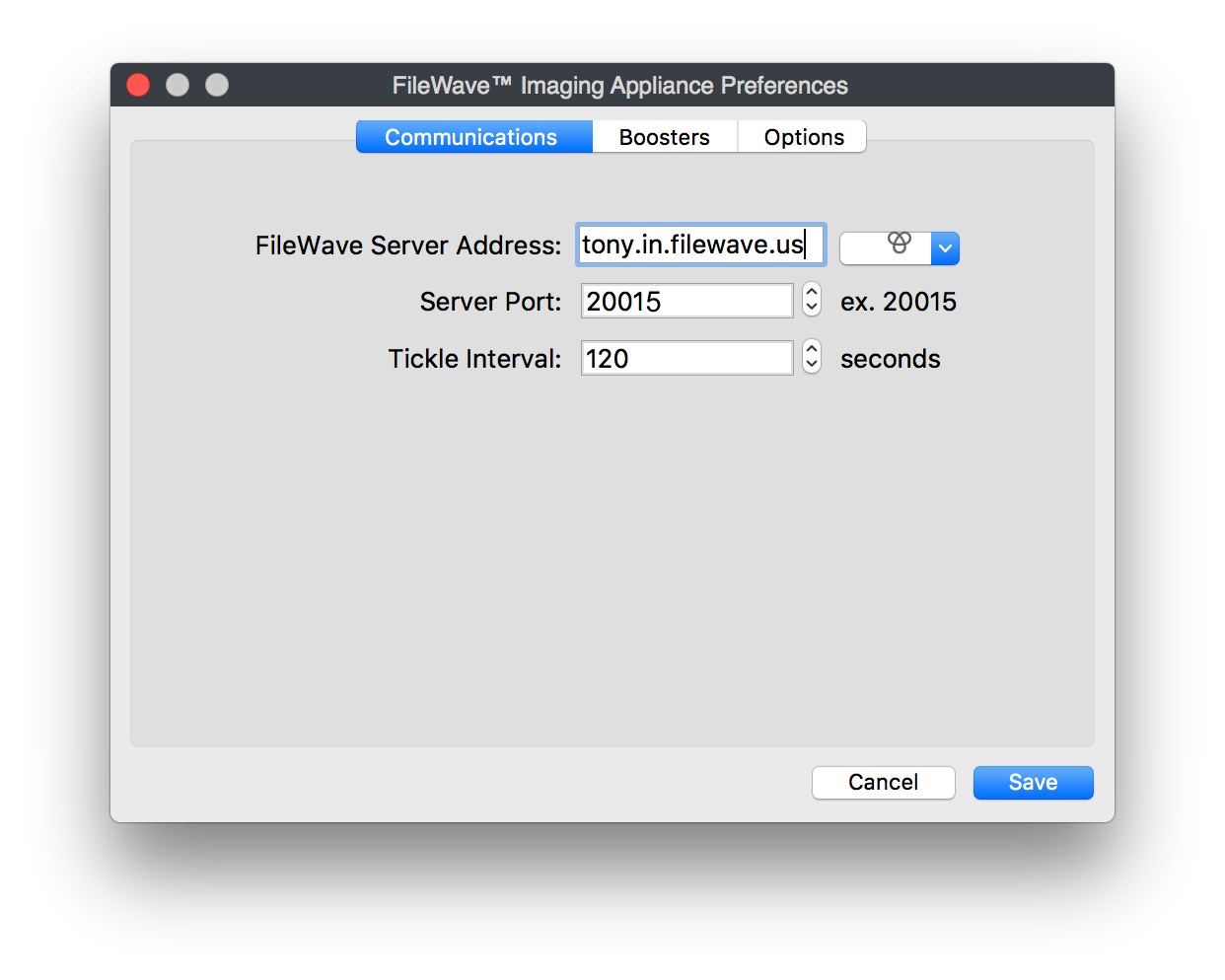
- When the Imaging Monitor opens specify your FileWave Server Address and Port 20015. Confirm by clicking "Ok" to finish configuration of your IVS.
-
Restart the Imaging Virtual Server (IVS)
-
Open the preferences and go to the "Imaging" tab again
-
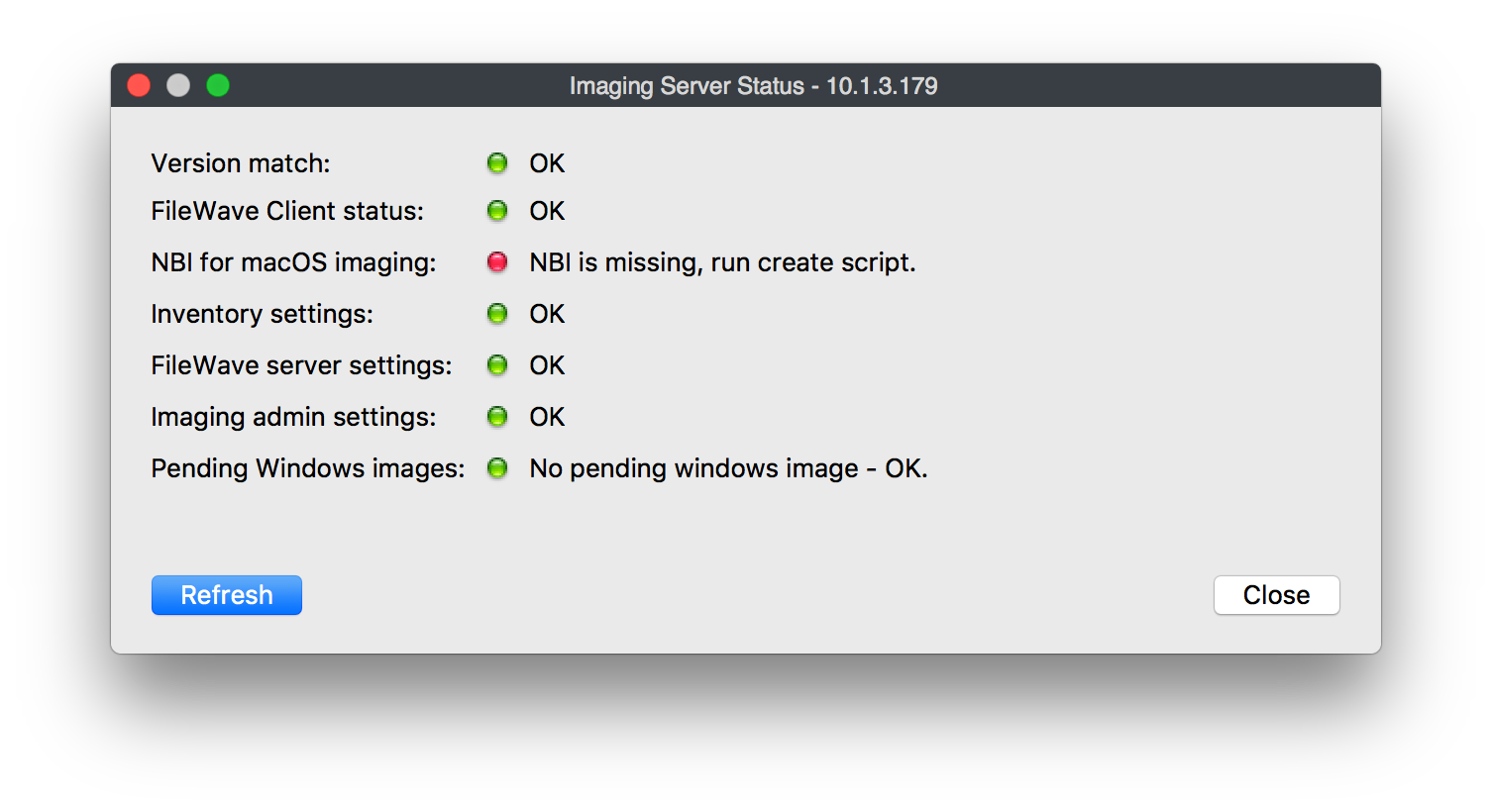
Select the server in the pane and click the status button below. Status lights should be all green with the exception of "NBI for macOS Imaging:" (If there are more red lights and clicking the refresh button doesn't help, please contact support)
Congratulations, you have successfully set up and configured your FileWave Imaging server! You are now ready to image Windows devices, Windows Network Imaging - Capturing and Deploying Images

No comments to display
No comments to display